某客户部署在 DMZ 区的 SRX 345 防火墙之前是透明模式部署在网络内,现需要对其增加 4 层的安全策略,由于涉及到大量客户端与服务器通信的需求,以及服务器之间通信的需求,且网段规划不合理,网关在核心上,导致策略比较混乱。
整体配置策略调试花了三周左右,期间多次更改策略,需要和客户核对,并且需要对接多个部门负责应用的人确认业务的流量。
SRX 的命令网络工程师看还可以,但是客户对防火墙不是很了解,所以需要自动化的方式将策略整理为其他形式,例如 excel 的方式更直观,同时准确性也得到了保证,这一点非常重要。
一条策略包含如下内容
-
policy-name
-
from-zone
-
to-zone
-
source-address
不是直接写地址,而是 address-book 或 address-set
-
destination-address
同 source-address 一样
-
application
-
action
-
address-set
包含一个或多个address-book
-
address-book
包含一个地址或域名
-
-
获取 SRX 策略的配置
Juniper 的 Junos 可以输出多种配置方式,例如 set 类型的配置命令、xml、json(12版本不支持),为使代码有更强的适应性,使用了 xml 格式的源配置文件
如下代码定义一个函数将 xml 转为 json 格式,方便分析
def xml_to_json(xml_str): xmlparse = xmltodict.parse(xml_str) jsonstr = json.dumps(xmlparse, indent=1) return jsonstr
-
获取 address_book 与 address_set
-
def get_address_book(): finnal_address_list = [] # os.chdir('/Users/houmingming/cache') with open('SRX345config.xml') as file: j = json.loads(xml_to_json(file.read())) address_book_raw = j['rpc-reply']['configuration']['security']['address-book'] for x in address_book_raw['address']: try: finnal_address_list.append([address_book_raw['name'], x['name'], x['ip-prefix'], 'ip-prefix']) except KeyError: finnal_address_list.append([address_book_raw['name'], x['name'], x['dns-name']['name'], 'dns-name']) address_book_set = address_book_raw['address-set'] for x in address_book_set: for i in x['address']: for y in finnal_address_list: if i['name'] == y[1]: y.insert(1, x['name']) for x in finnal_address_list: if len(x) == 4: x.insert(1, 'None') return finnal_address_list
def get_address_set(): # os.chdir('/Users/houmingming/cache') with open('SRX345config.xml') as file: j = json.loads(xml_to_json(file.read())) address_book_raw = j['rpc-reply']['configuration']['security']['address-book']['address-set'] finally_address_set = [] for x in address_book_raw: for i in x['address']: # print(i['name']) finally_address_set.append([x['name'], i['name']]) return finally_address_set
-
-
分析策略
从字典中获取策略包含的元素,并返回一个列表
def policy_analysis(): with open('SRX345config.xml') as file: j = json.loads(xml_to_json(file.read())) finally_policy = [] for value in j['rpc-reply']['configuration']['security']['policies']['policy']: for x in value['policy']: try: for i in x['then'].keys(): finally_policy.append([x['name'], value['from-zone-name'], value['to-zone-name'], x['match']['source-address'], x['match']['destination-address'], x['match']['application'], i]) except TypeError: print(value) return finally_policy
-
写入到数据库内
写入数据库的优点是可以很多种方式调用,例如放到网站上,也可以导出为 excel
def write_to_db(): conn = psycopg2.connect(dbname="houm01db", user="houm01dbuser", password="packet@123", host="docker.houm01.com") cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute("truncate table app01_example_srx_address_book") for x in get_address_book(): cursor.execute("INSERT INTO app01_example_srx_address_book (name, address_book,address,type )" "VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s)", (x[0], x[2], x[3], x[4])) cursor.execute("truncate table app01_example_srx_address_set") for y in get_address_set(): cursor.execute("INSERT INTO app01_example_srx_address_set (address_set, address_book_name )" "VALUES (%s, %s)", (y[0], y[1])) cursor.execute("truncate table app01_example_srx_policy") for i in policy_analysis(): cursor.execute("INSERT INTO app01_example_srx_policy " "(policy_name, source_zone, destination_zone, source_address, destination_address, application, action) " "VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s)", (i[0], i[1], i[2], str(i[3]), str(i[4]), str(i[5]), i[6])) conn.commit() cursor.close() conn.close()
-
创建 excel 并写入
每个策略方向一个工作表,address-book 和 set 各一个工作表
同时做了一些调整字体、间距的操作
def policy_to_excel(): conn = psycopg2.connect(dbname="houm01db", user="houm01dbuser", password="packet@123", host="docker.houm01.com") cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute("select policy_name, source_zone, destination_zone, source_address, destination_address, application, action from app01_example_srx_policy where action != 'log'") data = cursor.fetchall() cursor.execute("select * from app01_example_srx_address_set") address_book_set_data = cursor.fetchall() cursor.execute("select * from app01_example_srx_address_book") address_book_data = cursor.fetchall() cursor.close() conn.close() book = xlwt.Workbook(encoding='utf-8') worksheet = book.add_sheet('SRX 345 policy') address_book_set_sheet = book.add_sheet('address_book_set') address_book_sheet = book.add_sheet('address_book') # 初始化自定义的style tittle_style = xlwt.XFStyle() mystyle = xlwt.XFStyle() # 定义标题字体 tittle_font = xlwt.Font() tittle_font.name = 'Times New Roman' tittle_font.height = 20 * 14 tittle_font.bold = True # 定义正文字体 font = xlwt.Font() font.name = 'Times New Roman' font.height = 20 * 12 font.bold = False # 加粗 # 定义居中方式 al = xlwt.Alignment() al.horz = 0x02 al.vert = 0x01 # 定义背景颜色 pa = xlwt.Pattern() pa.pattern = xlwt.Pattern.SOLID_PATTERN pa.pattern_fore_colour = 47 tittle_style.font = tittle_font tittle_style.alignment = al tittle_style.pattern = pa mystyle.font = font mystyle.alignment = al # 定义表头 worksheet.write(0, 0, label='policy-name', style=tittle_style) worksheet.write(0, 1, label='from-zone', style=tittle_style) worksheet.write(0, 2, label='to-zone', style=tittle_style) worksheet.write(0, 3, label='source-address', style=tittle_style) worksheet.write(0, 4, label='destination-address', style=tittle_style) worksheet.write(0, 5, label='application', style=tittle_style) worksheet.write(0, 6, label='action', style=tittle_style) address_book_set_sheet.write(0, 0, label='address-set', style=tittle_style) address_book_set_sheet.write(0, 1, label='address-book-name', style=tittle_style) address_book_sheet.write(0, 0, label='name', style=tittle_style) address_book_sheet.write(0, 1, label='address-book', style=tittle_style) address_book_sheet.write(0, 2, label='address', style=tittle_style) address_book_sheet.write(0, 3, label='type', style=tittle_style) # 定义内容 val = 1 for x in data: worksheet.write(val, 0, str(x[0]), style=mystyle) worksheet.write(val, 1, str(x[1]), style=mystyle) worksheet.write(val, 2, str(x[2]), style=mystyle) worksheet.write(val, 3, str(x[3]), style=mystyle) worksheet.write(val, 4, str(x[4]), style=mystyle) worksheet.write(val, 5, str(x[5]), style=mystyle) worksheet.write(val, 6, str(x[6]), style=mystyle) val = val + 1 val = 1 # 重置 val 值 for y in address_book_set_data: # print(y) address_book_set_sheet.write(val, 0, str(y[1]), style=mystyle) address_book_set_sheet.write(val, 1, str(y[2]), style=mystyle) val = val + 1 val = 1 # 重置 val 值 for z in address_book_data: # print(z) address_book_sheet.write(val, 0, str(z[1]), style=mystyle) address_book_sheet.write(val, 1, str(z[2]), style=mystyle) address_book_sheet.write(val, 2, str(z[3]), style=mystyle) address_book_sheet.write(val, 3, str(z[4]), style=mystyle) val = val + 1 # 设置宽度 # 宽的基本单位是256,所以用乘法的方式,容易查看 worksheet.col(0).width = 256 * 30 worksheet.col(1).width = 256 * 12 worksheet.col(2).width = 256 * 10 worksheet.col(3).width = 256 * 50 worksheet.col(4).width = 256 * 50 worksheet.col(5).width = 256 * 30 address_book_set_sheet.col(0).width = 256 * 15 address_book_set_sheet.col(1).width = 256 * 30 address_book_sheet.col(0).width = 256 * 10 address_book_sheet.col(1).width = 256 * 30 address_book_sheet.col(2).width = 256 * 30 address_book_sheet.col(3).width = 256 * 15 # 行高的基本单位为20 serial = 0 while serial < len(address_book_data) + 1: worksheet.row(serial).height_mismatch = True # 设置行高可以修改 address_book_set_sheet.row(serial).height_mismatch = True address_book_sheet.row(serial).height_mismatch = True worksheet.row(serial).height = 20 * 20 address_book_set_sheet.row(serial).height = 20 * 20 address_book_sheet.row(serial).height = 20 * 20 serial = serial + 1 book.save('example_srx345_policy.xls')
def session_analysis(): with open('/Users/houmingming/cache/srx/SRX345log.txt') as file: raw_txt = file.read() raw_txt.index('nnode0:n---') # 查找node0的所在位置 raw_txt.index('nnode1:n---') # 查找node1的所在位置 node0_session = raw_txt[raw_txt.index('nnode0:n---'):raw_txt.index('nnode1:n---')] node1_session = raw_txt[raw_txt.index('nnode1:n---'):] split_node0_session = re.split('Session ', node0_session) # 利用 re.split 切分字符串,以 "Session" 这个字符来切 # 该正则将所有内容都匹配上了,但只使用其中一部分 re_session = re.findall('.*ID: (.*), Policy name: (.*)/(.*), State: (.*), Timeout: (.*), (.*)n In: (.*)/(.*) --> (.*)/(.*);(.*), Conn.*If: (.*), Pkts: (.*), Bytes: (.*), n Out: (.*) --> (.*)/(.*);(.*), Conn.*If: (.*), Pkts: (.*), Bytes: (.*), ', node0_session) return re_session
def session_into_db(): conn = psycopg2.connect(dbname="houm01db", user="houm01dbuser", password="packet@123", host="docker.houm01.com") cursor = conn.cursor() insert_time = input("请输入获取session的时间,格式示例'2019-11-10 10:00':n") for i in session_analysis(): cursor.execute("INSERT INTO app01_example_srx_session " "(insert_time, session_id, policy_name, policy_seq, state, source_ip, source_port, destination_ip, destination_port, protocol, source_interface, destination_interface)" "VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s)", (insert_time, i[0], i[1], i[2], i[3], i[6], i[7], i[8], i[9], i[10], i[11], i[18])) conn.commit() cursor.close() conn.close()
-
排列方法,做调用
if __name__ == '__main__': code = input('请选择要执行的功能n' '选择"1":分析SRX的xml文件,并插入到数据库n' '选择"2":生成策略Excel文件n' '选择"3": 分析Sessionn') if code == "1": write_to_db() elif code == "2": policy_to_excel() elif code == "3": session_into_db() else: print("输入错误,已退出")
-
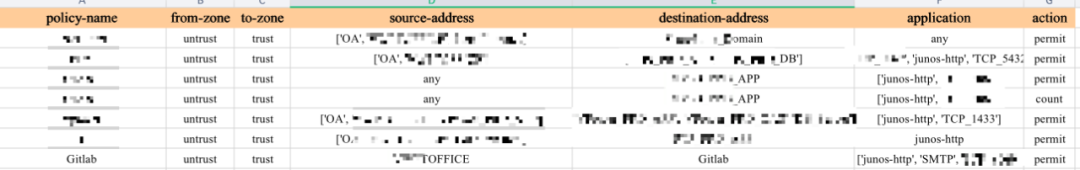
输出后的 excel 部分内容如下